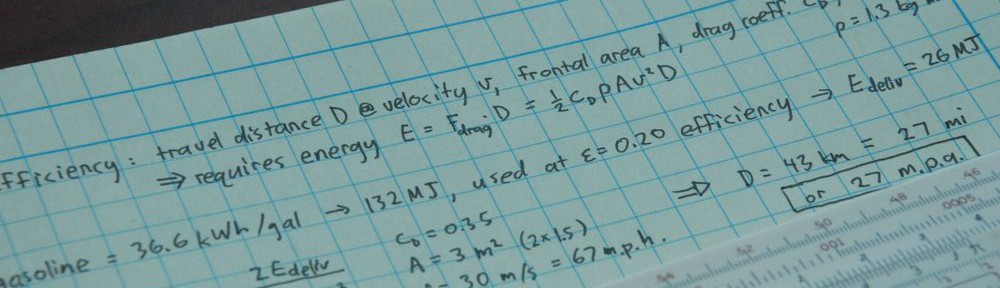[An updated treatment of some of this material appears in Chapter 2 of the Energy and Human Ambitions on a Finite Planet (free) textbook, also mirrors a 2022 article in Nature Physics..]
Some while back, I found myself sitting next to an accomplished economics professor at a dinner event. Shortly after pleasantries, I said to him, “economic growth cannot continue indefinitely,” just to see where things would go. It was a lively and informative conversation. I was somewhat alarmed by the disconnect between economic theory and physical constraints—not for the first time, but here it was up-close and personal. Though my memory is not keen enough to recount our conversation verbatim, I thought I would at least try to capture the key points and convey the essence of the tennis match—with some entertainment value thrown in.
Cast of characters: Physicist, played by me; Economist, played by an established economics professor from a prestigious institution. Scene: banquet dinner, played in four acts (courses).
Note: because I have a better retention of my own thoughts than those of my conversational companion, this recreation is lopsided to represent my own points/words. So while it may look like a physicist-dominated conversation, this is more an artifact of my own recall capabilities. I also should say that the other people at our table were not paying attention to our conversation, so I don’t know what makes me think this will be interesting to readers if it wasn’t even interesting enough to others at the table! But here goes…
Continue reading →
Views: 85197
 What do you get when you cross an astronomically-inclined physicist with concerns over energy efficiency in lighting? Spectra. Lots and lots of spectra. In this post, we’ll become familiar with spectral characterization of light, see example spectra of a number of household light sources, and I’ll even throw in some mind-blowing photos. In the process, we’ll evaluate just how efficient lighting could possibly be, along the way understanding something about the physiology of light perception and the definition of the increasingly ubiquitous lighting measure called the lumen. Buckle your physics seat-belt and prepare to think like a photon.
What do you get when you cross an astronomically-inclined physicist with concerns over energy efficiency in lighting? Spectra. Lots and lots of spectra. In this post, we’ll become familiar with spectral characterization of light, see example spectra of a number of household light sources, and I’ll even throw in some mind-blowing photos. In the process, we’ll evaluate just how efficient lighting could possibly be, along the way understanding something about the physiology of light perception and the definition of the increasingly ubiquitous lighting measure called the lumen. Buckle your physics seat-belt and prepare to think like a photon.